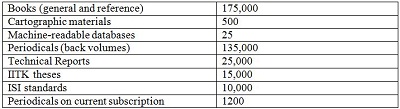
Awareness and Use Patterns of Online Journals and Databases: A Study of P. K. Kelkar Library at the Indian Institute of TechnologyKanpurAbstractObjective: The present study sought to determine use of online journals and databases and to assess current user characteristics associated with use of online resources at the Indian Institute of Technology-Kanpur (IITK) P. K. Kelkar Library. Methodology: The study is based on questionnaire method. A questionnaire was distributed among the faculty members, research scholars, and postgraduate students to collect desired data. Findings: A total of 240 questionnaires were distributed to the selected sample for the session 2010-11; 160 valid samples were collected. The result showed a growing interest in online journals among the users at IITK P. K. Library. The survey found that the majority of the respondents of IITK P. K. Library showed key interest in use of various databases like Science Direct, Web of Science, IEEE/IEE/IEL Online and the others for various purposes. Awareness among the users about the availability of online journals was found satisfactory. Online journals were mostly used for research needs and PDF was the most preferred format. There are many factors that may affect the use of scholarly online journals 1. IntroductionThe web resources and the use of web as a tool is changing the way users live and learn. In the early phase, the World Wide Web was mainly used for push type applications to provide information and resources to users. The recent development of Web 2.0 and the spread of open sources and shared use concepts have focused on user-generated content and applications for sharing. This led to additional development and popularity of web resources. Remote access to online journals has been a major boon to academic and research libraries. Online journals are considered a central feature of any librarys collection and have become indispensable for research in any field. The quantity of online journals is growing larger and has become a quite visible component of serial publication. Numerous academic institutions are currently building substantial collections of full-text journals and continue to increase access to various online databases. Many online journals and databases are available through open access. However, for those that are not available via open access, subscription to online journals and databases through the consortium(s) are much more economical for the libraries than individual purchase. IIT KanpurThe Indian Institute of Technology-Kanpur (IITK) carries out original research and technology development. It trains students to be competent, motivated engineers and scientists. The Institute not only celebrates freedom of thought, cultivates vision, and encourages growth, but also inculcates human values and concern for the environment and society. The rapid growth of electronic information resources changed and is still changing the IITK academic communitys information-seeking behavior as they search for resources to support their teaching, research, and extension activities. Effective use of these electronic resources for retrieving needed information will have a profound impact, especially on the quality of research output by IITK scholars. P. K. Kelkar LibraryP. K. Kelkar Library (formerly Central Library) of IITK is an academic library with a collection of more than 300,000 volumes and subscriptions to more than 1000 periodicals. The abstracting and indexing periodicals, microform and CD-ROM databases, technical reports, standards, and theses are important parts of this collection. Each year, an average of 4500 books and journal volumes are added to the collection. The total collection breakdown is as follows: 1.2. Earlier StudiesA large number of studies of users of online journals have appeared in the last few years. Tenopir (2002), in a major survey of the literature on the subject, analyzed the results of over 200 studies of the use of electronic resources in libraries published between 1995 and 2003. Results drawn from this literature survey indicate that electronic resources have been rapidly adopted in academic spheres, though the behaviors related to this adoption vary according to the discipline. In a significant study, Jamali, Nicholas, and Huntington (2005) presented the conclusions of several studies that used log analysis to study the use and users of electronic journals. These papers focused on the formats preferred by the end users, and documented that the users preferred PDF rather than HTML format. This study also noted the growing preference for searching (as opposed to browsing) as the main means of accessing information. Bar-Ilan and Fink (2005), in a study particularly important to this paper, presented the following findings: The results of these studies will enable the inference of many interesting features. The major finding is as follows:
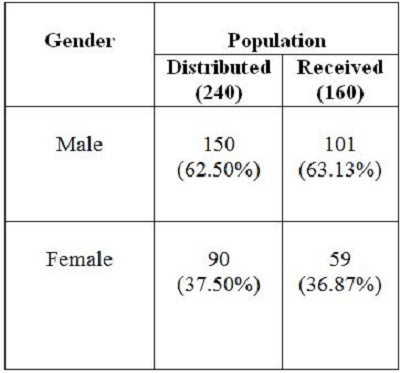
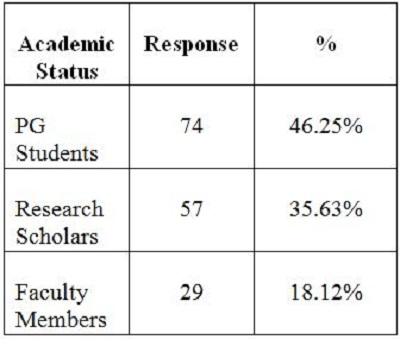
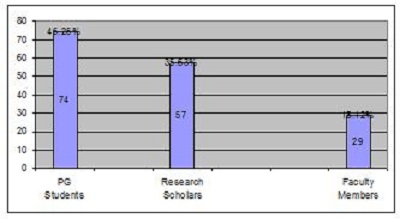
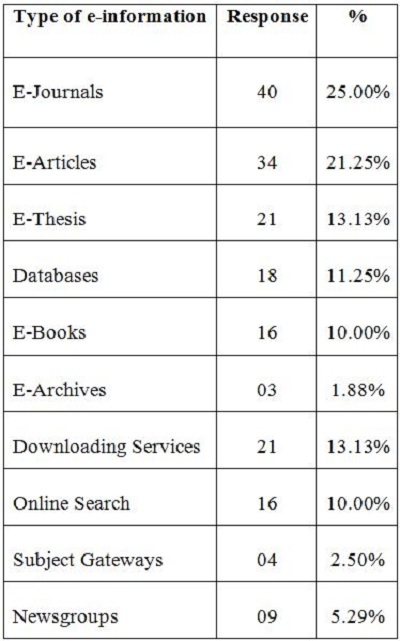
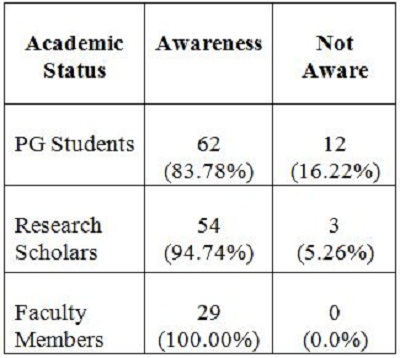
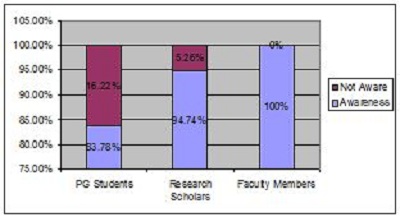
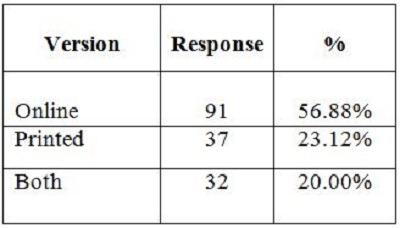
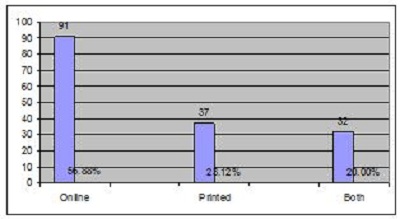
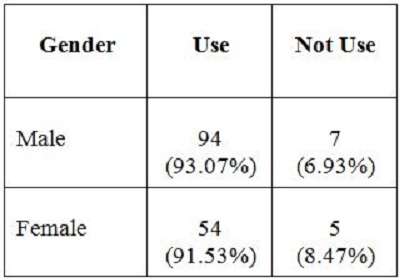
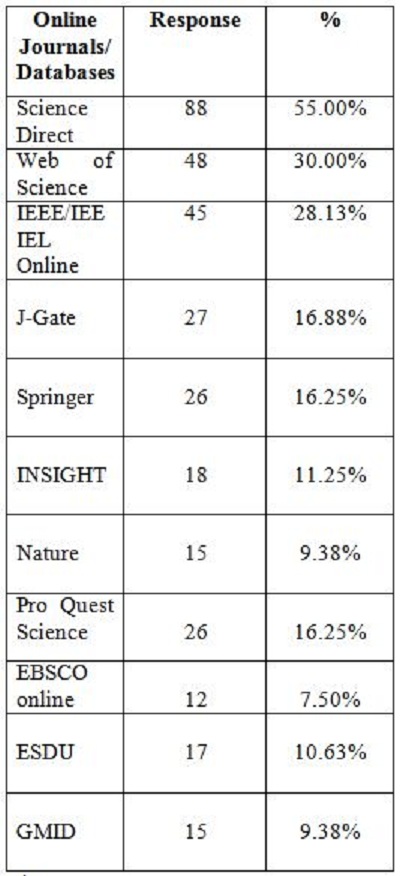
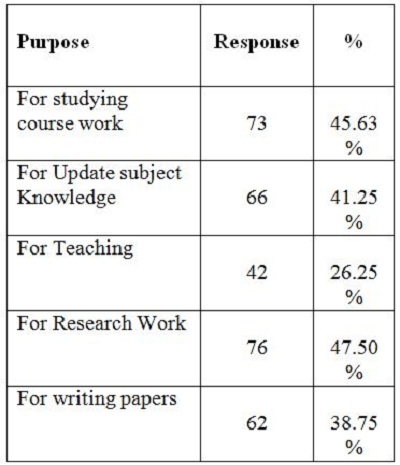
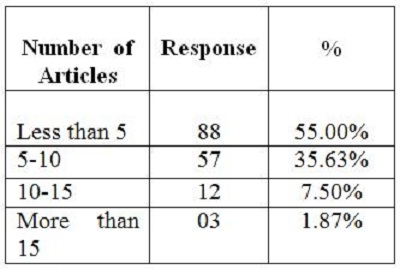
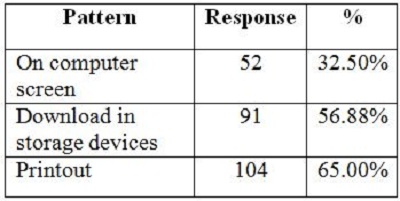
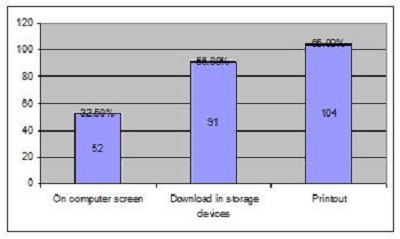
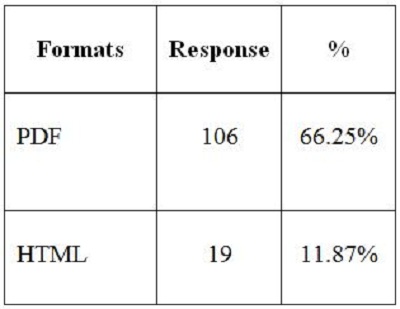
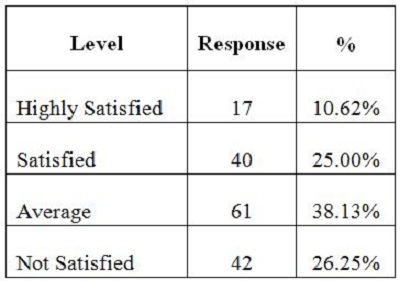
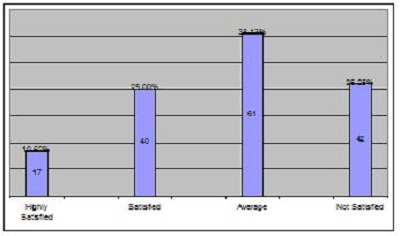
2. Objectives of the StudyIn the present study, the main objective is to examine the use of online journals and the databases by the postgraduate students, research scholars and faculty members of IITK. This study aims to identify users' opinion of different features of online journals, their awareness of the online journals' services, their awareness of user awareness programs, their use of different publishers, the purpose and components of this use, their training needs, and their preferred formats. 3. MethodologyA survey method based on a questionnaire was used for this study. The questionnaire was constructed around the following elements: user profile, awareness of online journals and databases, frequency of use, and reasons for use or non-use. The revised questionnaire was administrated to the 240 users of the IITK. Out of 240 questionnaires distributed, 160 responses were received (66.67%). 4. Analysis of data4.1 Sample PopulationUser profile section of the questionnaire provides information regarding the gender and different academic status (as can be seen from Figure 1 and Figure 2). Of the population studied, 63.13% were males and only 36.87% of the total were females (Figure 1). PG students constituted 46.25% of the respondents, 36.65% were research scholars and only 18.12% were faculty members (see Figure 3). 4.2 Use of Electronic Information ResourcesThe results show that 25.00% of the respondents prefer electronic journals while 21.25% prefer electronic articles (see Figure 4). The respondents use the electronic information resources mostly for research purposes. 4.3 Awareness of Online Journals and DatabasesFigure 5 provides the results for the respondents' awareness of online journals and databases available through the library. Of the faculty members, 100% were aware about the online journals, 94.74% research scholars were aware, whereas only 83.78% of postgraduate students were aware of the availability of online journals. 4.4 Preference Level of Using Online JournalsThe results reveal that 56.88% of respondents prefer the online-only version of journals. Only 23.12% of users prefer printed journals. 20.00% of respondents prefer to use both online and printed journals (see Figure 7). 4.5 Use of Online Journals and DatabasesBased on questionnaire responses, 93.07% of the males and 91.53% of the females used online journals for a variety of different purposes (see Figure 9). 4.6 Most Used and Useful Online Journals and DatabasesScience Direct is the most used and useful journal for the scientific community, with a 55% use rate. The table also shows the other most used and useful online journals and databases (see Fig. 10). 4.7 Purpose of Using Online Journals and DatabasesAccording to the findings, 47.50% of respondents use online journals and databases for their research work, 45.63% use it for course-related studying, 41.25% use online journals for updating subject knowledge, and 26.25% use online journals and databases for teaching (see Figure 11). 4.8 Articles Read in a WeekThe majority of the respondents (55%) read less than 5 online journal articles in a week, and 35.63% of respondents read 5-10 articles per week. Very few of the respondents (1.87%) read more than 15 articles in a week (see Figure 12). 4.9 Linking Pattern of Online JournalsIt was observed from the analysis that a majority (65.00%) of the respondents make a printout after using online journals. A significant portion of respondents (56.88%) download the content with storage devices, mostly with pen drives, and 32.50% of respondents use on the computer screen (see Figure 15). Online Journals are available in two major formats, PDF and HTML. Most respondents (66.25%) preferred PDF format for using online journals, whereas 11.87% of respondents preferred HTML format (see Figure 17). Majorities (73.75%) of respondents are satisfied with the infrastructure provided by the library for accessing online journals and their databases at different levels whereas only 26.25% of respondents are not satisfied (see Figure 19). The results of the study offer significant information on the level of awareness and use of electronic journals, the characteristics of the users and their evaluation of the journal collection. Interestingly, the users have knowledge of the availability of electronic journals, but many use them as only a supplementary way to access information. Many users are unconvinced of the potential of the electronic journals. However, the preference for the electronic format is related to the discipline and age of the respondents and is higher among those with academic status. The present survey reflects a growing interest in online journals among the users at IITK. This study reveals that most users are aware of the availability of online journals through the library and they are able to make maximum use of them for various purposes. The analysis of online journals shows that Science Direct (55.00%) is the most popular among the users. A large number of participants understand that the number of electronic journals is increasing and the number of print versions is decreasing, and accordingly resort to the electronic format. Many participants also revealed that they use the print format occasionally. We observed that doing research increases the opportunity for using electronic journals. The purpose for using online journals and databases is mainly for research work, followed by studying course work and updating subject knowledge. This study shows that the PDF is the most preferred format for online journals. Very few users prefer HTML format. This study has also shown that online journals and databases are mostly accessed at the library. The level of satisfaction among the respondents regarding the infrastructure provided by the library for accessing online journals and databases indicates that a majority of users (73.75%) are satisfied with the existing infrastructure. Based on the findings of the study, the following suggestions are put forward to improve the use of electronic information sources among the users of IITK P. K. Kelkar Library: Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. (n.d.). Retrieved February 19, 2011, from http://www.iitk.ac.in/ P K Kelkar Library, Indian Institute of Technology Kanpur. (n.d.). Retrieved February 19, 2011, from http://library.iitk.ac.in/index1.html Sunil Tyagi has been associated with the Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission, Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Government of India, Ghaziabad (UP), India for the last 2 years. He obtained his MLISc degree with a gold medal from Ch. Charan Singh University, Meerut, UP. He is a member of the Delhi Library Association and Kerala Library Association. He has published over 27 research papers and almost 20 review papers and book articles. |
Contents
|
 international · peer reviewed · open access
international · peer reviewed · open access